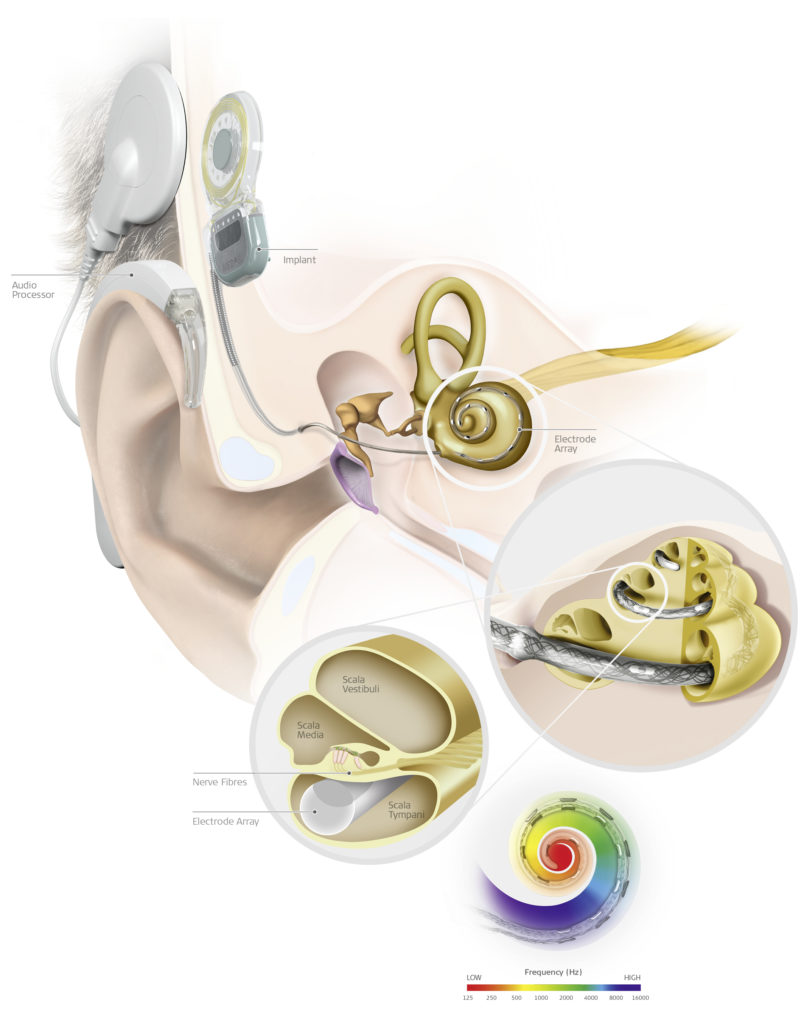
A cochlear implant (CI) is a medical device that can be implanted in the inner ear to enable profoundly deaf people to gain a sense of hearing. This digital sensory prosthetic offers an alternative when a hearing aid is no longer effective, as it turns sound vibrations into electrical pulses that stimulate a person’s hearing nerve.
A microphone on the device’s external part receives sound and passes it through a micro-computer that digitises and converts it into electrical signals. The signals are then sent through an electrode array implanted inside the person’s cochlea, where the current directly excites the hearing nerve cells. In doing so, the implant almost entirely replaces the function of the inner ear’s damaged hair cells. These electrical signals are then transported through the hearing nerve to the hearing areas of the brain where they are processed and interpreted. This process enables CI users to hear sounds.